Bad sleep habits? – 10 Tips to Improve Your Sleep Hygiene
 Andrew Jolie March 19, 2024 11 min read
Andrew Jolie March 19, 2024 11 min read
Sleep hygiene - it plays a bigger role in your physical and mental well-being than you might think. Unfortunately, many people suffer from poor sleep hygiene, with some global studies suggesting up to 50-60% struggle with insomnia.
So, what is good sleep hygiene and how can you reach it? It all comes down to your routines. Maintaining healthy sleep habits help you to make changes that stand the test of time.
In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know for a restful sleep - from pinpointing the signs of bad sleep habits to our best sleep hygiene tips.
Article in brief
- Sleep hygiene refers to the day-to-day sleep habits that affect your sleep quality
- Healthy sleep hygiene can improve your mental and physical well-being
- Developing good sleep habits keeps your sleep hygiene consistent
- Signs of poor sleep hygiene include daytime sleeping, struggling to sleep at night, and sleep disturbances
- Small, incremental changes can improve your sleep hygiene, including through structured sleep routines, reducing caffeine intake, and wearing a sleep mask
What is sleep hygiene?
Put simply, sleep hygiene refers to the daily habits and routines that affect how you sleep. People can have either healthy sleep hygiene or bad sleep hygiene, depending on their habits.
These sleep habits are related to both your daytime and nighttime routines. So, for example, what you eat during the day and when you eat it can affect your sleep hygiene.
Why is sleep hygiene important?
Sleep hygiene practices ensure that you get a better night’s sleep. Healthy sleep patterns have a knock-on impact on both mental and physical health.
For example, did you know that sleep deficiency has been found to change activity in certain parts of the brain? Poor sleep habits are associated with poor critical thinking and emotional regulation, as well as depression and suicide.
There’s also a strong link with many chronic health conditions, including diabetes, heart disease and obesity.
Meanwhile, taking care to practice proper sleep hygiene can help to manage, improve and prevent these issues from developing.
But good sleep hygiene isn’t built overnight. Sporadic attempts at getting a restful sleep won’t give you the foothold you need for consistent bedtime bliss. What makes sleep hygiene so special is that it relies on the power of habits.
Why are good sleeping habits essential for sleep hygiene?
Habits are a great way to maintain long-term behavioral change. Studies have shown they help healthy behaviors to remain consistent over time, enacted on autopilot. They’re especially effective when the changes are small and incremental, rather than big changes all at once.
It’s essential to keep the rhythm of your routines going. One study found that it took 66 days on average to build small healthy-eating habits, with more complex behaviors taking longer. Don’t blame yourself if your new good sleep habits don’t set in right away, or if you miss a day. Keep going and you’ll find your habits grow naturally.
Use our sleep hygiene checklist PDF to keep yourself motivated as your positive habits grow.
Bad Sleep Habits: Signs of Poor Sleep Hygiene
Unfortunately, just as good sleeping habits can grow, so too can bad habits. If you’re experiencing poor sleep hygiene, this will be reflected in your habitual behaviors.
Signs of poor sleep hygiene include:
- Feeling tired or falling asleep during the day
- Waking up in the night
- Struggling to get to sleep
- General fatigue throughout the day
- Feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep
- Sleep disturbances
- Snoring or choking when you wake up (sleep disorder symptoms)
- Insomnia
- Feeling irritable
- Overeating
As these responses to lack of sleep continue, they can create a cycle fueled by bad sleeping habits. For example, if you’re struggling to sleep at night, you might stay up looking at your phone, which can then make it even harder to sleep.
10 tips and techniques to improve sleep hygiene?
If you’re worried about your sleep hygiene, don’t fear. It’s better to make small changes slowly, so you’re more likely to stick to them. Below we’ve listed some simple ways to improve sleep hygiene.
Develop a structured nighttime routine
Let your body know it’s time to settle down and sleep with a structured routine. This can help you to sleep faster and more restfully.
Keep consistent times for going to bed at night and waking up in the morning. Ensure that these times allow you to get the recommended 7+ hours of sleep.
Try to incorporate a set routine of mindful actions at least 30 minutes before bed to help your body wind down. This could include:
- mindfulness meditation
- sleep journaling
- listening to soothing music
- reading a physical book (not ebooks!)
Looking for some nighttime reading? Print off and read our sleep hygiene tips PDF to help you get some extra ZZZs.
Turn off your devices an hour before bed
It’s no secret that using phones, tablets, laptops, and other electronic devices can make you more alert. They also produce blue light, which can reduce your melatonin levels (a hormone that helps your body to sleep). That’s why it’s best to avoid them for at least an hour before bed - and even turn them off altogether, if possible.
Reduce caffeine intake
Caffeine stimulates the brain, so naturally it can keep you awake at night. Try to avoid caffeinated drinks in the evening. Keep your intake to the mornings, if possible. Remember that around six hours after drinking caffeine, half of it will still remain in your system.
Avoid food and drink before bed
Aim to eat around two to three hours before going to bed. This ensures that your body is able to digest your food before you sleep. It’s also best to just drink water in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Practice self-care and exercise during the day
Maintaining good sleep habits doesn’t just matter at night. What you do with your day can also impact your sleep quality and quantity. Daily 30-minute exercise routines are an important priority. Exercise can reduce the impact of sleep disorders, and it’s especially effective on sleep when done outdoors in natural sunlight.
Keep your daily naps to a minimum too. Limit yourself to 30-minute naps, and avoid them altogether in the late afternoon.
Create a relaxing sleep environment
To improve sleep hygiene, your bedroom should also be restful. This includes:
- Keeping your bedroom at a cool but comfortable temperature
- Blocking outside light as much as possible
- Investing in the right pillows and mattress to suit your needs
- Tidying your room to create a minimal, relaxing space
- Wearing earplugs and listening to white noise to block out outside noise
Don’t hit snooze on your morning alarm
It's tempting to set multiple alarms in the morning, then turn them on to snooze if you want to go back to sleep. Unfortunately, that's not helpful for your sleep hygiene.
It's far better to set clear, designated times to wake up and stick to them. Repeatedly waking up and going back to sleep can affect your natural sleep cycle and potentially make you feel even groggier when you wake up.
Avoid tossing and turning
When you're trying to sleep, you might think the best option is always to lie down in bed. But that's not always good sleep hygiene. Tossing and turning can reinforce the idea that your bed isn't a restful space.
If you find you really can't sleep, it's more beneficial to sit up and read a book or practice mindfulness until you feel ready to sleep again.
Don’t use your bed for work
Restful associations are essential if you want to form good sleeping habits. If your body associates your bed with stress and work, then it's less likely to settle down for sleep. Don't be tempted to take your laptop to bed with you, whether to finish an assignment or send a quick work email. You should also aim to avoid any stressors before bedtime, including social media platforms.
Use a sleep mask
Whilst it’s best to avoid some types of technology before bed, sleep masks are an important exception. Sleep masks are comfortable, wearable masks that help you to maintain healthy sleep hygiene through neurofeedback.
The Bía sleep mask measures your brain activity using Functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS), so that it can develop a deep understanding of your sleep patterns. After the measurement is complete, it then responds by sending out neural music tuned to your brain’s activity.
This is played back via Spheric Sound, where small vibrations in the mask’s foam layer are picked up as sound in your brain. This type of foam-conduction audio has an additional benefit of calming your Vagus nerve, which takes care of your heart and respiratory rates, reducing stress and improving your sleep quality.
Learn more about the cutting-edge science behind Bía sleep masks.
FAQs about improving sleep hygiene:
What is considered good sleep hygiene?
Good sleep hygiene involves setting up healthy habits to facilitate a good night’s sleep. This will typically include:
- Developing a relaxing bedroom space with limited light
- Reducing electronics use and caffeine before bed
- Establishing a consistent nighttime routine
- Avoiding eating before bed
- Maintaining an active daily life
You could remember this by the acronym, “DREAM”. However, to some extent, healthy sleep hygiene will depend on the person. Experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you.
What is considered poor sleep hygiene?
Poor sleep hygiene doesn’t look the same for everyone. However, there are some key bad sleep habits associated with poor sleep hygiene:
- Not getting the recommended amount of sleep per night
- Waking up regularly at night
- Lack of exercise during the day
- Napping regularly during the day
- Engaging with electronic devices within an hour before bed
- Sleeping on an uncomfortable bed with busy surroundings
- Drinking caffeine or alcohol before bed
What is the healthiest sleep pattern?
There are several different sleep patterns, and the healthiest pattern for you will depend on your needs. The main different patterns are:
- Monophastic sleep - This is the most common sleep pattern, potentially influenced by modern industrial working hours and the use of electronic devices. It involves sleeping in one block period (ideally between 7-9 hours).
- Biphastic sleep - In this pattern, people sleep for a shorter period at night (typically between 5-6 hours) and also have a short sleep of up to 90 minutes during the day. This is the normal sleeping pattern in some countries, particularly in Latin American and the Mediterranean.
- Segmented sleep - This is a type of biphastic sleep where there are still two sleeping periods, but both are at night.
- Polyphasic sleep - This refers to sleep patterns that involve more than two sleeping periods across the day and night.
What are the best habits that ensure a healthy sleep hygiene?
Though they will vary between individual sleepers, the best healthy sleep habits include:
- Setting a consistent bedtime routine
- Avoiding screens for at least 1 hour before bed
- Adopting a healthy exercise routine during the day
- Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake
- Using a sleep mask to regulate your sleeping patterns
- Waking up when your morning alarm goes off (rather than hitting snooze!)
What is the 10 3 2 1 0 rule for sleep?
The 10-3-2-1-0 rule is a simple set of guidelines for good sleep hygiene. It encourages you to set several simple sleep habits for a more restful sleep. These are:
- Stop drinking caffeine 10 hours before bedtime
- Restrict your food and drink 3 hours before bedtime
- Finish your work 2 hours before bedtime
- Avoid screens 1 hour before bedtime
- Press the snooze button 0 times on your alarm
What is the healthiest sleep cycle?
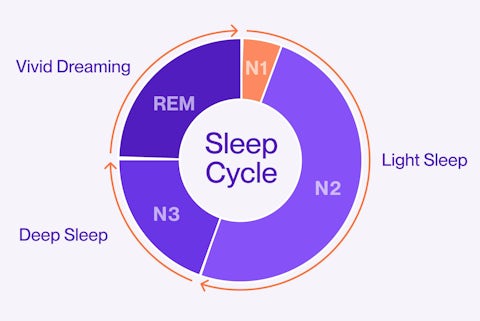
Through our sleep, we experience several rounds of the sleep cycle. This sleep cycle is built into four stages.
- NREM Stage 1 (N1) - This is the first stage of sleep, where the body and brain begin to slow down.
- NREM Stage 2 (N2) - This is another light sleeping stage, where your breathing and heart rate slow, your muscles relax, and your body temperature goes down.
- NREM Stage 3 (N3) - Also known as “deep sleep”, this stage of sleep is restorative to the body and mind, supporting the immune system and repairing tissue, among other essential functions.
- REM Sleep - Known for the rapid eye movement that occurs during this stage, REM sleep features increased brain activity and vivid dreams. It’s associated with improvements in cognitive functioning.
The healthiest sleep cycle would allow enough time for all of these stages, which can be achieved through improved sleep hygiene.
What are the benefits of sleep education?
Sleep education helps you to understand what healthy sleep hygiene looks like. You can use this information to adjust your sleeping habits and adapt your bedtime routines. Keeping up to date about how sleep impacts your mental and physical wellbeing ensures you can unlock its benefits.
If you’d like to develop your sleep education, you can read our good sleep hygiene PDF for a clear overview. Plus, there’s a wealth of information to be found in our online sleep blog.
How can I improve my sleep wellbeing?
Simple ways to improve your sleep wellbeing include establishing a clear bedtime routine, avoiding phones and laptops before bed, avoiding food and caffeine in the hours before you sleep, and utilizing a sleep mask for a more restful sleep.