Insomnia – Why Can’t I Sleep? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
 Andrew Jolie February 06, 2024 8 min read
Andrew Jolie February 06, 2024 8 min read
Are you having trouble sleeping consistently well, or suffering from sleepless nights?
You may suffer from insomnia, which is more widespread than ever in today’s fast-paced, data-ridden world.
What is Insomnia?
Insomnia, a prevalent sleep disorder, affects approximately 1 in 3 adults worldwide, according to the Cleveland Clinic, significantly impacting their daily lives.
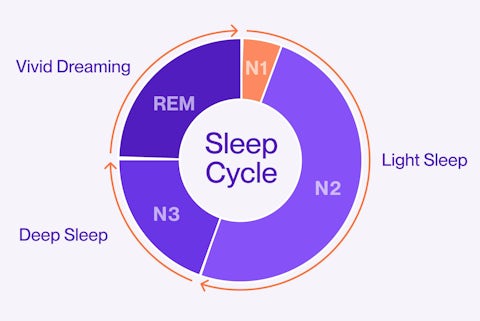
This sleep disorder involves trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or getting deep sleep, which results in problems functioning during the day. It can be separated into various types based on duration and severity:
- Acute Insomnia: This type is short-term, often triggered by stress or life events, and can last from a few days to a few weeks.
- Chronic Insomnia: Defined by its duration, chronic insomnia occurs at least three nights a week for three months or longer. Long-term stress, lifestyle habits, or other health conditions can cause it.
- Severe Insomnia: While not always a separate category, severe insomnia refers to the intensity of sleep disruption and its impact on daily life. It can be part of either acute or chronic insomnia but significantly impairs your functionality.
- Clinical Insomnia: This term is typically used in research and healthcare settings to describe insomnia that meets specific diagnostic criteria and may require clinical intervention for management.
Understanding the differences is important for diagnosing and treating insomnia effectively, tailoring approaches to the specific type and underlying causes.
Why Can’t I Sleep?
Understanding the factors and causes of your insomnia is crucial because it allows for targeted and effective treatment. By pinpointing the specific cause, you can address the root of your sleep issues rather than just the symptoms. This approach improves the chances of restoring healthy sleep patterns and enhances overall well-being. Recognizing what triggers insomnia is the first step in creating a personalized plan to combat it, possibly leading to more successful outcomes and a better quality of life.
Some causes of insomnia include:
Stress
Stress is a leading cause of insomnia. Concerns related to work, school, health, money, or family matters can leave your mind buzzing at night, making it hard to fall asleep. Life stresses like losing someone close, getting sick, ending a marriage, or losing a job can also trigger insomnia.
Bad Sleep Habits
Bad sleep practices, such as not sticking to a sleep schedule, taking naps, doing exciting activities before bed, sleeping in an uncomfortable setting, or using your bed for work, eating, or TV, can affect your sleep. Smartphones and screens just before bed can also interfere with your sleep cycle.
Mental Health Disorders
Mental health issues like anxiety, depression, and PTSD can interfere with regular sleep. Insomnia itself can also lead to changes in mood and shifts in hormones, worsening mental health conditions.
Medications
Various health conditions, including asthma, diabetes, neurological disorders like Parkinson's disease, chronic pain, and acid reflux, may lead to insomnia. These medications may contain caffeine or other stimulants that affect sleep.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can cause insomnia, including asthma, diabetes, neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease, chronic pain, and acid reflux. Sleep apnea, where breathing stops intermittently at night, also causes poor sleep quality.
Caffeine, Nicotine, and Alcohol
Stimulants like nicotine and caffeine can make it tough to fall asleep. Alcohol can initially induce sleepiness, but it reduces your sleep quality and is likely to cause disturbances in sleep later in the night.
Eating Too Late in the Evening
Having a heavy or large meal before bed can cause discomfort from indigestion that interferes with your sleep. Spicy or acidic foods can cause you stomach trouble and heartburn.
Environmental Factors
Noise, light, a room that’s too hot or too cold, and an uncomfortable bed or pillow can interfere with sleep. Travel or work schedules that disrupt your body's circadian rhythms, such as jet lag from traveling across multiple time zones, and working late or early shifts, can also lead to insomnia.
Figuring out and dealing with what's causing your insomnia can greatly better your sleep.
Source: https://www.helpguide.org/articles/sleep/insomnia-causes-and-cures.htm
Insomnia in Women
Insomnia in women can be closely linked to hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. These stages cause fluctuations in hormones like estrogen and progesterone, leading to sleep disturbances like night sweats, hot flashes, and mood swings. Understanding these reasons is important to handle insomnia in women properly, and it often means using special methods that match their specific hormone changes.
Insomnia in Men
Work stress and lifestyle choices can seriously impact sleep for men. Staying up late for work, worrying about job-related issues, or having habits like smoking or drinking caffeine late in the day can make it hard to fall asleep or stay asleep. If men are having trouble sleeping, they need to look at these areas of their lives, as making changes can help improve their sleep.
Side Effects of Insomnia
Insomnia doesn't just make you feel tired; it can have many other effects on your body and mind. When you don't sleep enough, you might struggle to concentrate, remember things, or make decisions. It can make you feel moody or depressed and even weaken your immune system, making you get sick more easily. Over time, not sleeping well can increase your risk for more serious health problems like heart disease, high blood pressure, as well as diabetes. It can also make you gain weight because it messes with the hormones that control hunger. Getting enough good sleep is essential for keeping you healthy and feeling good.
Long-term untreated insomnia can lead to serious side effects and risks for both mental and physical health. Mentally, it can cause issues like depression, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating. Insomnia's physical dangers include a greater likelihood of getting heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and a weak immune system, which can make fighting infections difficult. Getting to the root of insomnia and treating it is crucial to avoid these health problems.
How to Treat Insomnia
Insomnia often requires a comprehensive approach that addresses symptoms and underlying causes. Here's a broader look at the treatments available:
- Behavioral Changes: Foundational steps include establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime ritual, and making your bedroom comfortable and free from distractions (like TV and smartphones). Limiting naps and avoiding eating heavy meals before bedtime is also helpful.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Insomnia: This structured program helps you identify and replace thoughts and behaviors that cause or worsen sleep problems with habits that promote sound sleep. Unlike sleeping pills, CBT-I addresses the underlying causes of insomnia.
- Medications: While not a first-line treatment, sleeping pills prescribed by a doctor can be used short-term when insomnia significantly affects your daily life. It's important to use these under strict medical guidance due to potential side effects and dependency.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Adjustments: Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the hours before bedtime, can have a positive impact. Staying active can help improve sleep quality, but avoiding intense workouts right before bed is wise.
- Relaxation Techniques: Activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can reduce stress and promote better sleep.
- Use of Sleep Aids: Besides lifestyle changes and therapies, sleep aids like a Smart Sleep Mask can be particularly effective. The Bía Smart Sleep Mask is designed to block out light completely and adds neural sounds, creating an ideal environment for sleep. This simple tool helps to signal to your body that it's time to sleep, enhancing the production of melatonin and improving overall sleep quality. For those battling insomnia, incorporating a smart sleep mask like Bía's can be a straightforward and non-invasive way to encourage better sleep patterns and contribute to a healthier sleep routine.
How to Prevent Insomnia
Preventing insomnia involves adopting habits and routines that promote regular, restful sleep. Here are some strategies (similar to treatment) to help prevent insomnia:
- Establish a Regular Sleep Schedule: Stick to consistent sleep and wake times daily.
- Create a Bedtime Ritual: Engage in relaxing activities before bed to signal your body it's time to sleep.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Make sure your sleeping area is dark, quiet, and kept at a comfy temperature.
- Limit Exposure to Screens: Avoid phones, tablets, and computers at least an hour before bedtime.
- Watch Your Diet: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol before sleeping.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can improve sleep, but avoid vigorous activity close to bedtime.
- Manage Stress: Use meditation, deep breathing, or journaling to reduce stress.
- Ask a Doctor: Talk to your healthcare provider about persistent sleep troubles.
FAQs about Insomnia:
How common is insomnia?
Insomnia is pretty common, affecting up to 30% of adults at some point in their lives. Chronic insomnia, where sleep troubles occur at least three times a week for three months or more, impacts about 10% of adults.
Why do people have insomnia?
People experience insomnia for various reasons, including stress, anxiety, poor sleep habits, hormones, medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors like diet and exercise.
What is the first stage of insomnia?
The first stage of insomnia involves difficulty falling asleep. People might lie in bed for a long time before they can finally drift off.
At what point is it considered insomnia?
It's considered insomnia when a person has trouble falling asleep or staying asleep or wakes up too early and cannot fall back asleep. This happens at least three nights a week for three months or longer.
Is insomnia a disease or a disorder?
Insomnia is classified as a sleep disorder. It's a condition that affects the quality, duration, and efficiency of sleep.
Is insomnia dangerous?
While not immediately dangerous, chronic insomnia can lead to long-term health issues, including increased risk of depression, anxiety, heart disease, and diabetes.
What is an insomniac?
An insomniac is a person who has insomnia. This term describes someone who regularly has difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.